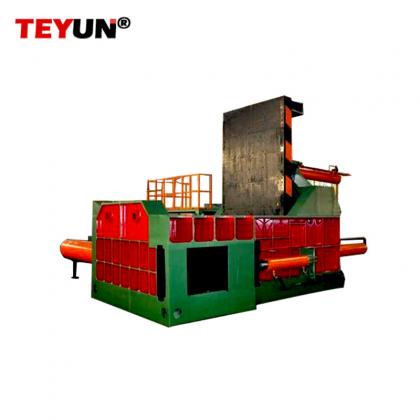
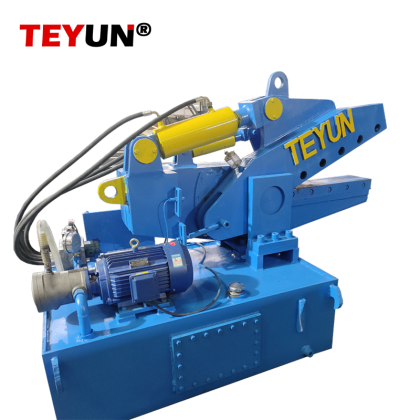
A metal shredder is a powerful industrial machine designed to process scrap metal into smaller, uniform fragments for efficient recycling. Utilizing high-torque rotating shafts fitted with hardened steel cutters, these robust systems tear and shear materials through a process known as shear shredding.
The primary function of a metal shredder is size reduction. It transforms large, unwieldy items like cars, appliances, and industrial waste into fist-sized pieces. This crucial step increases the material’s surface area, which subsequently streamlines downstream sorting and separation processes. Powerful magnets effectively extract ferrous metals (iron and steel), while eddy currents separate non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper.
The benefits of this technology are profound. Shredding significantly reduces the volume of scrap, lowering transportation and storage costs. It prepares material for remelting in furnaces with maximum efficiency, conserving energy and raw resources compared to virgin ore processing. This establishes the shredder as a cornerstone of the circular economy, ensuring valuable metals re-enter the manufacturing supply chain.
Furthermore, shredders enhance safety by destroying hazardous or sensitive materials, such as old electronics containing data-bearing components. Built to withstand extreme abrasion and impact, these machines are engineered for reliability and long-term operation, making them an indispensable asset for scrap yards and recycling facilities worldwide. Their operation is fundamental to promoting sustainable industrial practices and reducing environmental footprint. So how to choose a suitable for yourself?This is a question that many customers are concerned about.
1. Material Characteristics (Most Important Factor)
Metal Type: Is it thin aluminum cans or car hulls (light and thin metal) or heavy car engines, bicycle frames, or appliance housings (medium and thick metal)?
Composition: Does the material contain non-metallic materials? For example, plastic, rubber, or fabric in car debris. This can affect subsequent sorting and blade wear.
Final Output Requirements: What is the desired output size after shredding? Coarse shredding (50-100mm) or fine shredding (10-30mm)?
2. Capacity Requirements
Hourly Processing Capacity: How many tons of material do you expect to process per hour?
Working Format: How many hours per day will the machine operate? Will it be a single 8-hour shift or 24/7 continuous production?
3. Power System: Motor and Drive
Power: The required motor power is determined by the material hardness and production capacity requirements (ranging from tens of kilowatts to hundreds of kilowatts).
Drive Type: Common drive methods include direct motor drive, belt drive, and hydraulic drive. Heavy-duty shredders often use high-torque, slow-speed hydraulic drives or direct electric motors, which provide tremendous shredding force and strong impact resistance.
4. Cutterhead System (the Heart of the Equipment)
Cutterhead Material: The cutterhead must be made of high-strength alloy tool steel (such as H13) and undergo special heat treatment to ensure high hardness, wear resistance, and toughness.
Cutterhead Design: The arrangement of the moving and fixed blades, the shape of the blade hooks, and the gap adjustment all affect shredding efficiency and output size.
Maintainability: Is the cutterhead easy to remove and replace? A well-designed cutterhead housing should be easy to open and maintain.
5. Control System
Control System: Modern PLC control systems offer features such as automatic control, overload protection, reverse rotation, and fault alarms, greatly improving operational convenience and safety.

 Address : Mingjue Industry Park, Lishui District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province
Address : Mingjue Industry Park, Lishui District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province

 français
français русский
русский español
español العربية
العربية 日本語
日本語 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文















 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported